“Religion is a comprehensive system of belief that not only responds to human existential questions but also shapes laws, ethics, and social structures.”
— Max Weber, The Sociology of Religion (1922)
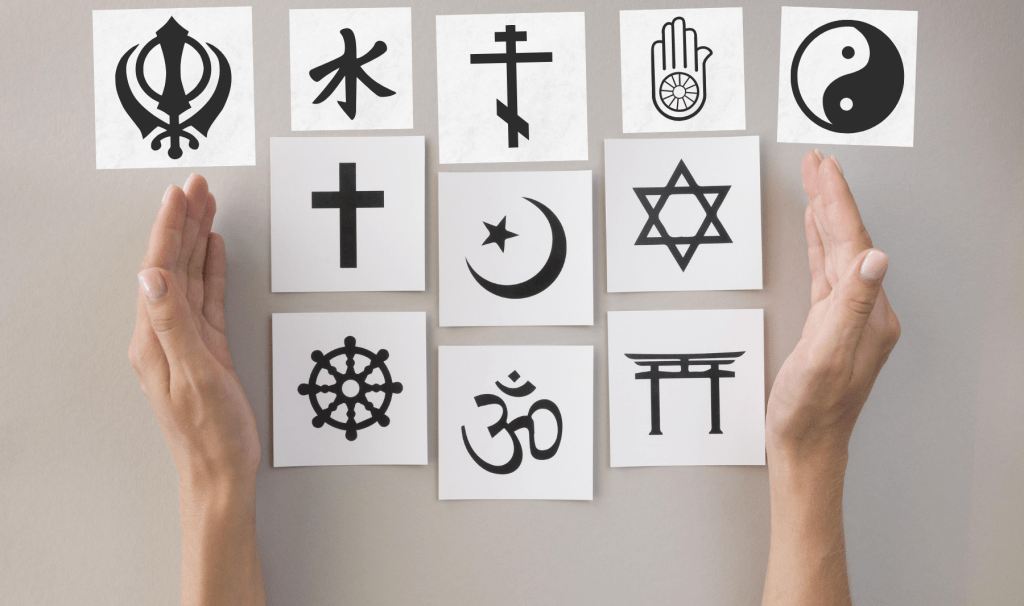
I have come across people who held all kind of different opinions about religion. The range expands form people who think of religion as a hindrance for society’s progress to people who think religion is what makes us civilized. I found people were very polarized about their view on religion. Some wanted to discard it completely from society as a useless remnant of past, while some wanted to protect the age old traditions forever. However I think religion is too intertwined with society and our lives to be discarded so easily.
It embodies a complex tapestry of influences that permeate through every dimension of human existence—spanning spirituality, ethics, community, culture, politics, and economics. By analyzing its far-reaching impact across these layers, we uncover the profound significance of religion in shaping individual lives and society at large. Its influence is not static but evolves with time, reflecting humanity’s changing needs and values.
Spirituality – The Heart of Religion
At its core, religion is deeply intertwined with spirituality, offering a path for individuals to explore the meaning of existence and their role within the world. This spiritual journey often leads to personal transformation, guiding people toward self-betterment and a higher purpose that transcends material pursuits. Religion provides a framework for grappling with life’s fundamental questions—what it means to be human, the nature of suffering, and the possibility of an afterlife.
In many traditions, this quest for meaning encourages a commitment to ethical living and self-discipline. It also fosters a sense of connection with something greater than oneself, whether that is understood as a divine being, cosmic force, or the interconnectedness of life.
Ethics & Morality
One of the most enduring contributions of religion to society is its role in shaping the ethical and moral standards. Across cultures, religious doctrines serve as a moral compass, guiding both personal behavior and societal norms.
Core values such as compassion, honesty, justice, and humility are central to many religions and provide a shared ethical framework that promotes social harmony. For instance, the concept of ahimsa in Hinduism and Buddhism emphasizes non-violence and respect for all living beings, influencing interpersonal relationships and community behavior.
Religion’s influence also extends to legal systems. Historically, many legal frameworks have incorporated religious principles, especially in areas like family law, inheritance, and social justice. While modern secular societies often advocate for the separation of religion and state, religious ethics continue to inform debates on moral issues such as abortion, capital punishment, and human rights.
“Religion is not only a social system but also a means of integrating different communities. It can offer a sense of belonging and identity, particularly in times of upheaval and crisis.”
— Emile Durkheim, The Elementary Forms of Religious Life (1912)
Community & Social Bonds
Religious institutions play a pivotal role in fostering social cohesion and building strong community bonds. Faith-based communities provide individuals with a sense of belonging and shared identity, offering support networks that are especially important in times of difficulty.
Beyond spiritual support, religious organizations are often at the forefront of charitable and humanitarian efforts. Whether through food banks, shelters, or disaster relief initiatives, they are instrumental in addressing societal needs, particularly for marginalized and vulnerable populations. In many cases, religious institutions serve as the backbone of social welfare systems, compensating for gaps in government services.
Moreover, rituals, festivals, and communal worship activities bring people together, reinforcing cultural continuity and creating a shared sense of purpose. The impact of these communal activities extends beyond religion, often shaping national identities and contributing to a society’s collective memory.
Cultural Practices & Identity
Religion is inseparable from cultural identity. It shapes rituals, customs, and traditions that permeate daily life and inform major life events—birth, coming of age, marriage, and death. Religious festivals like Diwali, Ramadan, and Christmas not only celebrate faith but also reinforce cultural heritage, creating a deep sense of belonging and shared history within communities.
Religion’s influence on culture extends into art, literature, and music, where it has inspired some of humanity’s greatest creative achievements. The Sistine Chapel, the Mahabharata, the Qur’an’s calligraphy, and countless religious hymns are not merely expressions of faith; they are cultural artifacts that have enriched the world’s artistic landscape. These works reflect and perpetuate the values, teachings, and narratives of their respective religions, ensuring their legacy within society.
Political & Social Influence
Religion’s influence on political structures and public policy is profound and historically embedded. Many societies have been governed by theocratic systems, where religious leaders wielded political power, while in other cases, religious ethics have directly informed governance. Even in contemporary secular states, religious ideologies shape public discourse and influence policies on critical issues such as education, healthcare, and human rights.
Religious organizations have also been pivotal in advocating for social justice. Figures like Martin Luther King Jr., Mahatma Gandhi, and Desmond Tutu used religious principles to spearhead movements for civil rights, anti-colonialism, and the fight against apartheid practice. Their moral authority lent credibility to these movements, mobilizing vast numbers of people and influencing public policy. Religion, when aligned with justice, has been a powerful force for societal transformation.
“Religion and politics are inseparable. Politics is the means by which we achieve collectively what we hold sacred. And religion is the conviction of those things worth sacrificing for.”
— Reinhold Niebuhr, Moral Man and Immoral Society (1932)
Economic Impact
Religion’s influence on economic activities is less frequently discussed but nonetheless it has a significant indirect influence. Religious institutions are major players in the global economy, running educational establishments, healthcare systems, and charitable foundations. In many countries, religious organizations are among the largest landholders and employers, with vast economic power.
The ethical principles promoted by religions often guide economic behavior of both individuals and institutions alike. Concepts such as zakat in Islam, dāna in Hinduism, and Christian tithing encourage charitable giving and philanthropy. Religious teachings also advocate for ethical business practices—such as fair wages, honesty in trade, and the prohibition of exploitation—highlighting the role of religion in shaping just economic systems.
Moreover, religious tourism, from pilgrimages to sacred sites like Mecca, Varanasi, or Jerusalem, generates significant revenue, contributing to local and national economies. Religious festivals also plays important role in the economic cycles and business all around the world eagerly wait for the spending boom during these festivals such as Christmas, Diwali and Ramadan.
Conclusion: The Integral Role of Religion in Society
Religion is not a monolithic entity, but rather a complex and multifaceted force that permeates every layer of society—from the intimate realm of personal spirituality to the broader influences on politics, culture, and economics. By exploring these dimensions—spirituality, ethical frameworks, community bonds, cultural identity, political influence, and economic impact—we gain a deeper understanding of the role religion plays in human life.
A more nuanced perspective of religion allows us to appreciate its contributions while critically examining how it intersects with modern societal challenges. Far from being an isolated aspect of life, religion continues to shape and be shaped by the world, influencing laws, ethical norms, and cultural practices in ways that are both subtle and profound.
Personal Note
My personal opinion about religion has travelled the entire spectrum, from one end of absolutely necessary to another end of absolutely useless, in a span of few years and now I sand exactly in the middle of the spectrum. The scope in this article is limited to influence of religion to different aspects of our lives and society. And these influences have mostly been analyzed through neutral or positive lens.
However this does not means that there are no negative side to religion. Just like any social construct religion too has it flaws. There have been countless wrongs done in the name of religion from wars to genocides. And quick glance back to our history tells us of many other inhumane atrocities and grave injustice committed in the name of religion. However I believe these negative manifestations are the result of few people misusing religion for their own gains and using it to justify things that could not stand the test of simple logic. Thus what role religion plays finally depend upon the people and their intentions.






Leave a comment